Collagen and gelatin are two closely related proteins that play essential roles in health and wellness. While both derive from animal connective tissues, they differ in structure and application. Understanding collagen vs gelatin helps consumers make informed choices for dietary and supplemental needs. This article explores their differences, benefits, and best uses.
You may also enjoy our protein gelatin recipe.
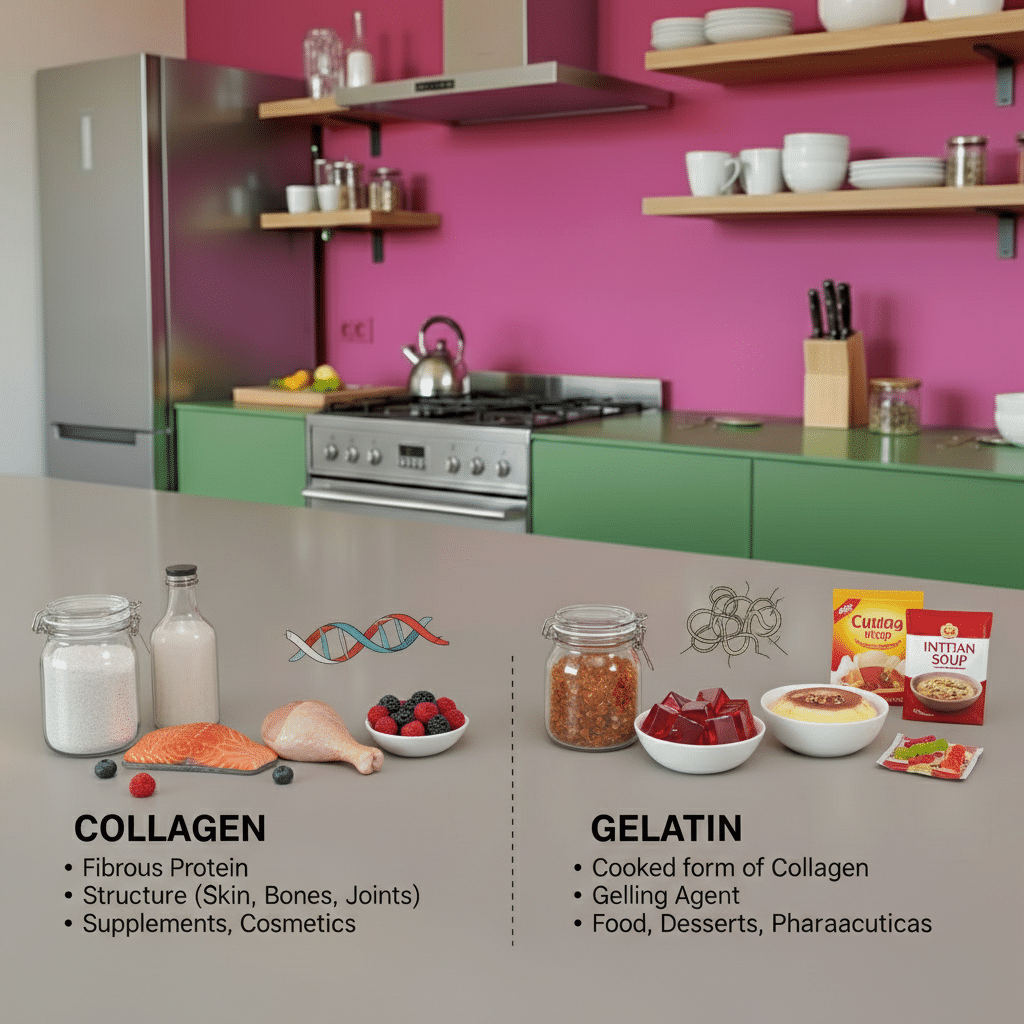
Collagen is the most abundant protein in the human body, providing structure to skin, bones, and joints. Gelatin, cooked form of collagen, widely used in food and pharmaceuticals. Both offer unique advantages, but their distinctions matter for specific health goals. Let’s dive deeper into what sets them apart.
Table of Contents
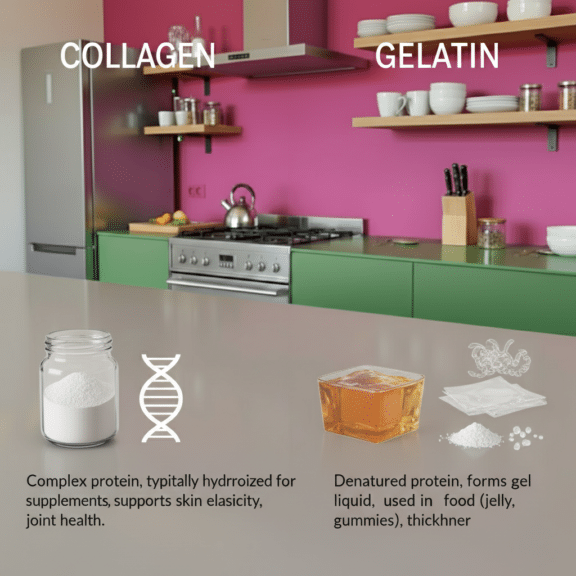
Collagen is a fibrous protein naturally found in skin, tendons, and bones. It supports tissue strength and elasticity. When collagen is heated or processed, breaks down into gelatin, which has a different molecular structure. This transformation alters how each functions in the body and in products.
See also: gelatin powder in desserts.
Gelatin dissolves in hot water and forms a gel when cooled, making it ideal for culinary uses. Collagen supplements, like hydrolyzed collagen peptides, remain soluble and are easily absorbed. Both provide amino acids, but their bioavailability and applications vary significantly.
Hydrolyzed collagen is further broken down for better digestion. It’s often used in powders and supplements. Gelatin, however, requires preparation to be effective. Knowing these differences helps determine which form best suits individual needs.
If you enjoyed this recipe, you might also like our perfect supplements gelatin.

Choosing between collagen and gelatin depends on intended use. Collagen supplements support skin, hair, and joint health without altering texture. Gelatin, however, preferred in recipes requiring thickening or gelling. Their distinct properties influence effectiveness in different scenarios.
For those seeking quick absorption, hydrolyzed collagen is optimal. Gelatin’s cooking requirements make it less convenient for daily supplementation. Both support protein intake, but collagen’s versatility in beverages gives it an edge for some users.
Looking for something similar? Try our gelatin jello.
Understanding these differences ensures optimal results. Whether for health or culinary purposes, selecting the right form maximizes benefits. The next sections explore variants and applications in detail.
Collagen comes in multiple types, with Type I, II, and III being most common. Type I supports skin and bones, while Type II benefits joints. Gelatin, derived from these types, varies based on source and processing. Bovine, marine, and porcine are popular sources.
If you enjoyed this recipe, you might also like our bariatric gelatin recipe.
Hydrolyzed collagen is processed into smaller peptides for easier absorption. Gelatin may be powdered, sheet-based, granulated. Each variant serves distinct purposes, from supplements to desserts. Below is a comparison of key forms:
| Type | Form | Primary Use |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrolyzed Collagen | Powder | Supplements, drinks |
| Sheets/Powder | Cooking, gelling |
Choosing the right variant depends on solubility, texture, and absorption needs. Hydrolyzed collagen blends seamlessly into liquids, while gelatin requires hydration. Understanding these differences aids in selecting the best option.

Discover more with our clear gelatin recipe.
Collagen supplements are popular for anti-aging and joint support. They mix easily into coffee, smoothies, water. Gelatin, however, excels in culinary applications like gummies, marshmallows, and soups. Both enhance protein intake but serve different functional roles.
In skincare, collagen peptides may promote elasticity and hydration. Gelatin’s gelling properties make it useful in capsules and coatings. Pharmaceuticals often use gelatin for its binding abilities, while collagen supplements target internal health benefits.
Discover more with our agar vs gelatin.
Athletes may prefer hydrolyzed collagen for muscle recovery. Gelatin’s amino acid profile supports gut health but requires preparation. Whether for cooking or wellness, each has unique advantages worth considering.
Collagen and gelatin share amino acids like glycine and proline. However, collagen peptides are smaller and more bioavailable. Gelatin forms gels, while collagen dissolves completely. These differences impact their suitability for various applications.
For more ideas, check out our guide on vegan gelatin.
For quick nutrition, collagen supplements are convenient. Gelatin requires heating to activate its properties. Both support joint and skin health, but collagen’s ease of use makes it a preferred supplement for many.
Below is a quick comparison of their key traits:
| Feature | ||
|---|---|---|
| Solubility | Cold-soluble | Heat-activated |
| Texture | Liquid-friendly | Gel-forming |
Choosing between them depends on desired outcomes. Collagen suits daily supplementation, while gelatin excels in recipes requiring structure.
Want to know more about the benefits of gelatin health? Check out this search.
Best Practices for Collagen vs Gelatin
For collagen supplements, consistency is key. Daily intake of 10-20 grams supports skin and joint health. Mixing with vitamin C enhances absorption. Gelatin should be hydrated in warm liquid before use to ensure proper gelling.
Store both in cool, dry places to maintain quality. Avoid high heat for collagen powders to preserve nutrients. Gelatin-based recipes should chill adequately for best texture. Following these practices ensures optimal results.
Learn more about gelatin benefits in this search.
Consulting a nutritionist can help tailor usage to individual needs. Whether for health or cooking, understanding proper handling maximizes benefits. Both collagen and gelatin offer valuable properties when used correctly.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between collagen and gelatin?
Collagen is a structural protein found in skin, bones, and connective tissues, while gelatin is derived from cooked collagen. The key difference is that collagen remains soluble in cold water, whereas gelatin forms a gel-like consistency when cooled.
Can collagen and gelatin be used interchangeably in recipes?
No, they serve different purposes in cooking. Gelatin is ideal for gelling desserts like jellies, while collagen peptides dissolve easily in liquids and are better suited for smoothies or soups without altering texture.
Which has more health benefits: collagen or gelatin?
Both offer similar amino acid profiles, but hydrolyzed collagen is more bioavailable, meaning the body absorbs it more efficiently. Gelatin provides gut health benefits due to its gelling properties.
How do collagen and gelatin support joint health?
Both contain glycine and proline, which help rebuild cartilage and reduce inflammation. Collagen supplements are often preferred for joint support because they’re easily absorbed.
Are collagen and gelatin derived from the same source?
Yes, both come from animal connective tissues, typically bovine or marine sources. Gelatin is produced by further breaking down collagen through boiling.
Can vegetarians use collagen or gelatin alternatives?
Traditional collagen and gelatin are animal-based, but plant-based alternatives like agar-agar or pectin can mimic gelatin’s texture in recipes. Vegan collagen boosters often contain silica or vitamin C to support natural collagen production.
Which is better for skin health: collagen or gelatin?
Collagen peptides are more effective for skin elasticity and hydration due to higher bioavailability. Gelatin still offers benefits but may require larger doses for similar effects.
How do collagen and gelatin affect digestion differently?
Gelatin soothes the gut lining and may aid digestion by attracting digestive juices. Collagen peptides are broken down faster, making them gentler for sensitive stomachs.
What are the best recipes using collagen or gelatin?
Gelatin shines in gummy candies, marshmallows, or aspic. Collagen blends well into coffee, smoothies, or baked goods without altering flavor or texture.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between collagen vs gelatin helps you choose the right option for your health and culinary needs. Collagen excels in bioavailability and skin benefits, while gelatin’s unique gelling properties make it indispensable in certain recipes. Both support joint health and digestion but cater to distinct applications. Whether you prioritize convenience in supplements or texture in cooking, recognizing their strengths ensures optimal results. For those exploring dietary adjustments, consider how each aligns with your goals—be it gut healing, anti-aging, or recipe versatility. Always consult a healthcare professional before making significant changes to your supplement routine.