Gelatin is a versatile ingredient that has been used for centuries in various applications, from food to pharmaceuticals. Understanding the different types of gelatin is essential for selecting the right one for your needs. Whether you’re a chef, health enthusiast, or a manufacturer, knowing the distinctions can make a significant difference in your results.
Table of Contents
You may also enjoy our gelatin jello.
This article delves into the various types of gelatin, their unique properties, and their respective uses. By the end, you’ll have a comprehensive understanding of how to choose the best gelatin for your specific requirements. Let’s explore the world of gelatin and uncover its many facets.
Gelatin is a protein derived from collagen, which is found in the connective tissues of animals. It is produced by boiling the skin, bones, and cartilage of animals, typically cows or pigs, extract the collagen. The extracted collagen is then processed to form gelatin, which is available in various forms such as powder, sheets, granules.
For more ideas, check out our guide on clear gelatin recipe.
The different types of gelatin are categorized based on their source, processing method, and properties. These variations determine their suitability for different applications, whether in cooking, medicine, industry. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for making informed decisions when using gelatin.
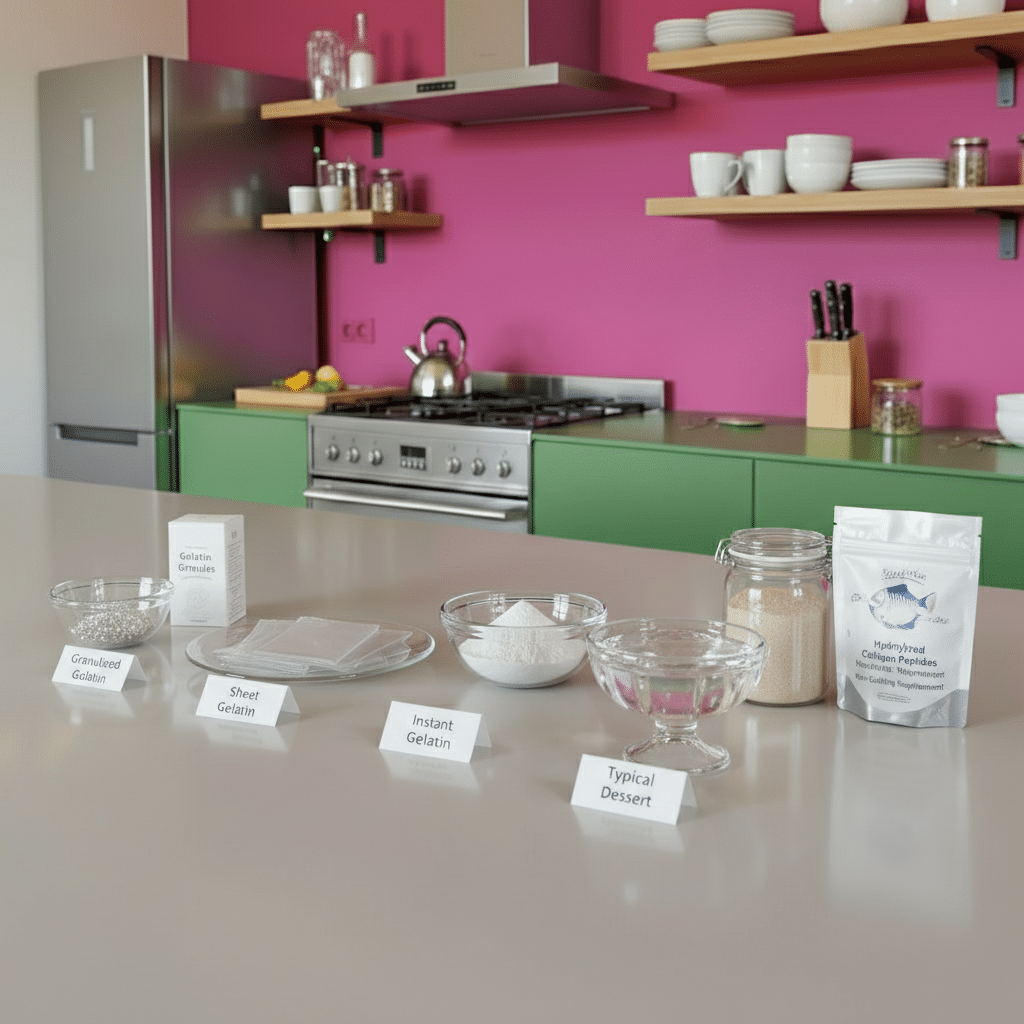

Gelatin is known for its gelling, thickening, and stabilizing properties, making it a popular ingredient in a wide range of products. Its unique characteristics are influenced by factors such as the animal source, extraction process, and the degree of hydrolysis. These factors contribute to the differences in texture, strength, and clarity among the various types of gelatin.
You may also enjoy our agar vs gelatin.
The type of gelatin you choose can significantly impact the outcome of your project. Different types of gelatin have varying gel strengths, melting points, and clarity, which can affect the texture and appearance of your final product. For example, a high-bloom gelatin is ideal for creating firm gels, while a low-bloom gelatin is better suited for softer textures.
In the food industry, selecting the right type of gelatin is crucial for achieving the desired consistency and stability in products like desserts, marshmallows, and gummy candies. Similarly, in the pharmaceutical industry, the choice of gelatin can influence the effectiveness and stability of capsules and coatings.
You may also enjoy our knox gelatin recipes.
Understanding the different types of gelatin also allows you to cater to specific dietary needs and preferences. For instance, halal and kosher-certified gelatin options are available for those who adhere to religious dietary restrictions. Additionally, plant-based alternatives are becoming increasingly popular among vegetarians and vegans.
There are several variants of gelatin, each with distinct characteristics and applications. The most common types include animal-derived gelatin, plant-based gelatin, and hydrolyzed gelatin. Animal-derived gelatin is further categorized based on the source, such as bovine, porcine, fish gelatin. Each type has unique properties that make it suitable for specific uses.
You may also enjoy our agar agar powder.
Plant-based gelatin, also known as agar-agar, derived from seaweed and is a popular alternative for vegetarians and vegans. Hydrolyzed gelatin, collagen peptides, is a broken-down form of gelatin that is easily absorbed by the body and is often used in dietary supplements. Each variant has its own set of benefits and limitations.
The following table provides a comparison of the different types of gelatin based on their source, properties, and common uses:
If you enjoyed this recipe, you might also like our perfect supplements gelatin.
| Type | Source | Properties | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bovine Gelatin | Cows | High gel strength, neutral flavor | Food, pharmaceuticals |
| Porcine Gelatin | Pigs | High gel strength, neutral flavor | Food, pharmaceuticals |
| Fish Gelatin | Fish | Lower gel strength, fishy flavor | Food, cosmetics |
| Plant-Based Gelatin | Seaweed | High gel strength, neutral flavor | Food, vegetarian products |
| Hydrolyzed Gelatin | Various | Easily absorbed, gelling properties | Dietary supplements |
Gelatin is widely used in various industries due to its unique properties. In the food industry, it is a key ingredient in products like gummy candies, marshmallows, and gelatin desserts. Its gelling and thickening abilities make it indispensable for creating the desired texture and consistency in these products. Gelatin is also used in dairy products like yogurt and cream cheese to improve texture and stability.
In the pharmaceutical industry, gelatin is used to make capsules and coatings for medications. Its biocompatibility and ability to dissolve in the digestive tract make it an ideal material for oral drug delivery. Gelatin is also used in the production of vaccines and other injectable medications as a stabilizer.
You may also enjoy our vegan gelatin.
Beyond food and pharmaceuticals, gelatin is used in the cosmetic industry for its skin-enhancing properties. It is a common ingredient in face masks, lotions, and creams due to its ability to improve skin elasticity and hydration. Gelatin is also used in photography, where it serves as a binder for light-sensitive materials.

In the arts and crafts industry, gelatin is used in the production of adhesives, coatings, and sizing agents. Its adhesive properties make it suitable for bookbinding, papermaking, and other crafts. Gelatin is also used in the production of biodegradable plastics and packaging materials.
If you enjoyed this recipe, you might also like our gelatin powder in desserts.
When comparing the different types of gelatin, it’s important to consider factors such as gel strength, melting point, clarity, and flavor. Bovine and porcine gelatin are similar in terms of gel strength and flavor, making them interchangeable in many applications. However, bovine gelatin is often preferred for its neutral flavor and higher clarity.
Fish gelatin, on the other hand, has a lower gel strength and a distinct fishy flavor, which limits its use in certain products. Plant-based gelatin, such as agar-agar, offers a high gel strength and neutral flavor, making it a popular alternative for vegetarians and vegans. Hydrolyzed gelatin lacks gelling properties but is easily absorbed by the body, making it ideal for dietary supplements.
Discover the benefits of gelatin here.
The choice of gelatin also depends on dietary restrictions and preferences. For example, halal and kosher-certified gelatin options are available for those who adhere to religious dietary laws. Additionally, plant-based gelatin is a suitable option for vegetarians and vegans who avoid animal-derived products.
Best Practices for types of gelatin
When using gelatin, it’s essential to follow best practices to achieve the desired results. Always measure the gelatin accurately, as the amount used can significantly impact the texture and consistency of your product. For powdered gelatin, it’s important to bloom it in cold water before dissolving it in hot liquid to ensure even distribution and proper hydration.
Curious about gelatin Uses? See the health benefits here.
Store gelatin in a cool, dry place to maintain its quality and shelf life. Exposure to moisture and heat can degrade the gelatin and reduce its effectiveness. When working with gelatin, avoid boiling it, high temperatures can break down the protein and weaken its gelling properties.
Consider the specific properties of the type of gelatin you’re using, such as gel strength and melting point, ensure it’s suitable for your application. For example, high-bloom gelatin is ideal for firm gels, while low-bloom gelatin is better suited for softer textures. Always test the gelatin in a small batch before scaling up to ensure the desired results.
Want to know more about the benefits of gelatin Applications? Check out this search.
Finally, mindful of dietary restrictions and preferences when selecting gelatin. Choose halal or kosher-certified options if necessary, and consider plant-based alternatives for vegetarian and vegan applications. By following these best practices, you can make the most of the different types of gelatin and achieve optimal results in your projects.

Frequently Asked Questions
What are the different types of gelatin available?
The main types of gelatin include animal-based gelatin (derived from collagen in animal bones and skin) and plant-based gelatin alternatives like agar-agar, pectin, and carrageenan. Each type has unique properties and uses in cooking and baking.
How is animal-based gelatin different from plant-based gelatin?
Animal-based gelatin is derived from collagen in animal parts, while plant-based gelatin is made from seaweed, fruit, or other plant sources. Plant-based options are vegan-friendly and often have different gelling properties.
Which type of gelatin is best for desserts?
For desserts, animal-based gelatin is commonly used due to its smooth texture and ability to set firmly. However, agar-agar is a popular plant-based alternative for vegan desserts.
Can you use powdered gelatin instead of sheet gelatin?
Yes, powdered gelatin can be used instead of sheet gelatin. However, they require different preparation methods, and the conversion ratio may vary depending on the recipe.
What are the health benefits of consuming gelatin?
Gelatin is rich in amino acids that support joint health, improve skin elasticity, and promote digestion. It’s also a source of protein and can aid in muscle recovery.
Is there a vegan alternative to traditional gelatin?
Yes, vegan alternatives to traditional gelatin include agar-agar, pectin, and carrageenan. These plant-based options are suitable for vegan diets and have similar gelling properties.
How do you prepare and use gelatin in recipes?
To prepare gelatin, soak it in cold water to bloom, then dissolve it in warm liquid. Follow recipe instructions carefully to ensure proper gelling and texture.
What are the common uses of gelatin in cooking?
Gelatin is commonly used in desserts like jellies, panna cotta, and marshmallows. It’s also used in savory dishes like aspic and to thicken sauces or soups.
How does gelatin affect the texture of food?
Gelatin creates a smooth, firm, and elastic texture in foods. It helps stabilize and thicken dishes, giving them a unique consistency that enhances the eating experience.
Can gelatin be used in cold dishes?
Yes, gelatin can be used in cold dishes, but it must be dissolved in warm liquid first and then cooled. Proper preparation ensures it sets correctly in cold recipes.
Conclusion
Understanding the different types of gelatin is essential for both cooking enthusiasts and health-conscious individuals. Whether you choose animal-based gelatin for its classic texture or opt for plant-based alternatives like agar-agar for vegan-friendly recipes, each type offers unique benefits. Gelatin’s versatility extends from desserts like jellies and panna cotta to savory dishes such as aspic, making it a staple in many kitchens. Beyond its culinary uses, gelatin provides health benefits like supporting joint health and improving skin elasticity. When preparing gelatin, proper techniques like blooming and dissolving ensure the desired texture and consistency. With this knowledge, you can confidently explore the many uses of gelatin in your cooking and baking endeavors. Next, consider experimenting with different types of gelatin in your favorite recipes to discover their unique properties.