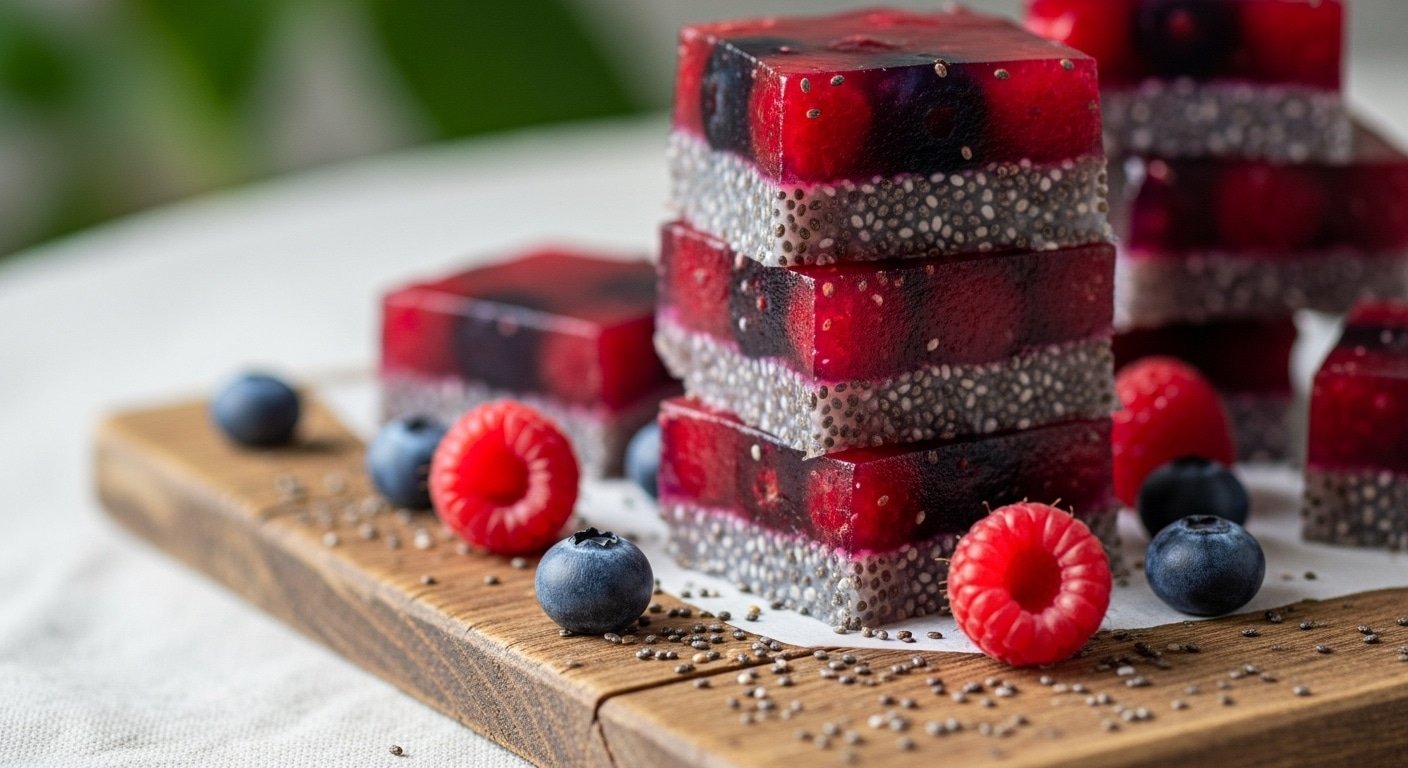
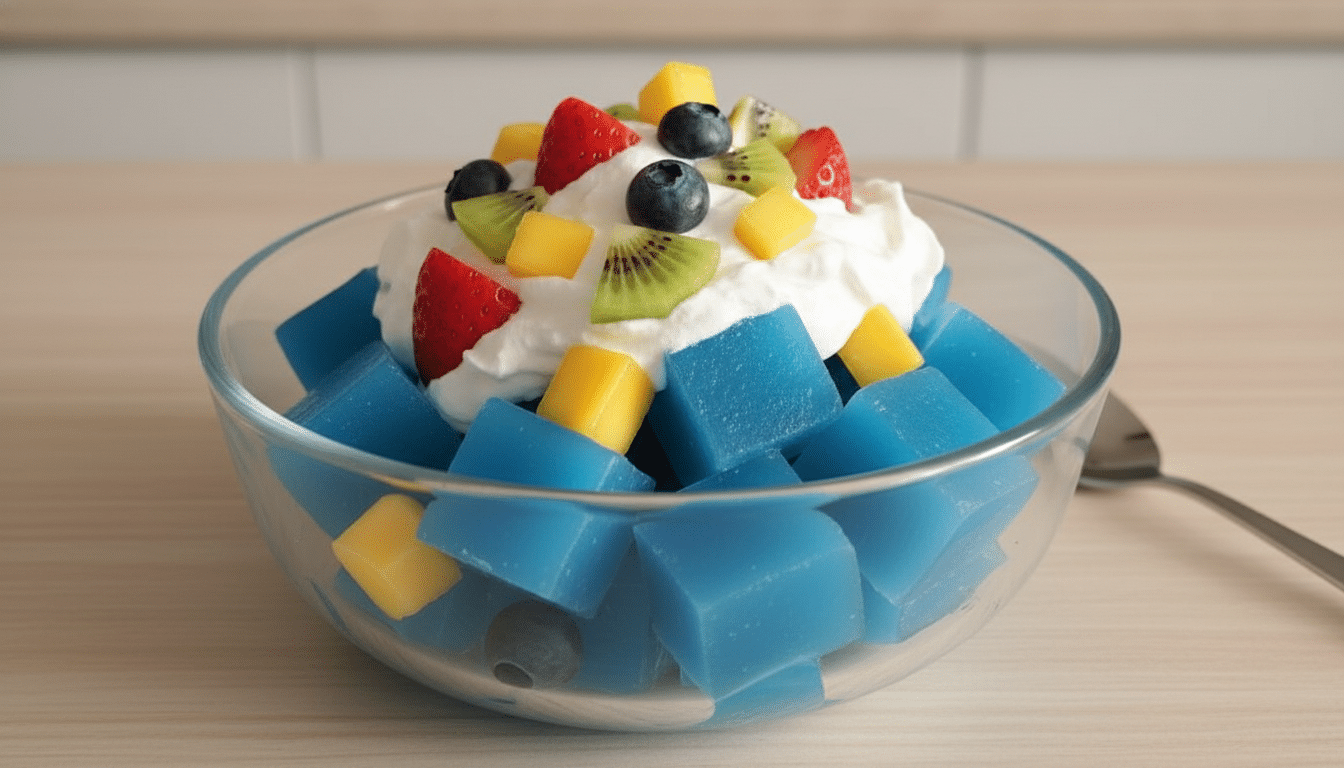
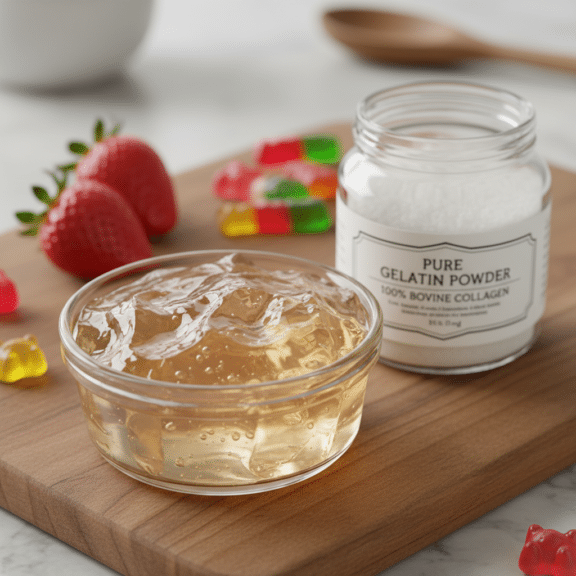
Gelatin is a protein derived from collagen, natural substance found in animal connective tissues. It is widely used in food, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics due to its gelling and thickening properties. Understanding what gelatin is helps consumers make informed choices about its applications and benefits.
Table of Contents

Discover more with our agar vs gelatin.
This article explores the origins, types, and uses of gelatin. Whether you’re curious about its role in cooking or its industrial applications, this guide provides a comprehensive overview. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of what gelatin is and why it matters.
Discover more with our vegan gelatin.
Gelatin is a translucent, flavorless substance obtained by boiling animal bones, skin, and connective tissues. The process breaks down collagen into gelatin, which solidifies when cooled. It is commonly available in powder or sheet form and is a staple in many culinary and non-culinary products.
Discover more with our gelatin jello.
The primary source of gelatin is pork, but it can also come from beef, fish, poultry. Vegetarian alternatives, like agar-agar, exist but differ in composition. Gelatin’s unique properties make it indispensable in recipes requiring texture modification, such as gummies, marshmallows, and desserts.
Discover more with our perfect supplements gelatin.
Beyond food, gelatin is used in pharmaceuticals for capsule coatings and in cosmetics for its moisturizing effects. Its versatility stems from its ability to form gels, stabilize emulsions, and retain moisture. These characteristics make gelatin a valuable ingredient across multiple industries.
You may also enjoy our gelatin powder in desserts.
Why Gelatin Matters
Gelatin plays a crucial role in food science, providing texture and stability to countless products. Without it, many candies, desserts, and processed foods would lack their familiar consistency. Its natural origin and functional benefits make it a preferred choice for manufacturers and home cooks alike.
If you enjoyed this recipe, you might also like our clear gelatin recipe.
In medicine, gelatin capsules are widely used for drug delivery due to their digestibility and neutral taste. They ensure accurate dosing and easy consumption, making medications more accessible. Gelatin’s biocompatibility also makes it useful in wound dressings and surgical applications.

Looking for something similar? Try our knox gelatin recipes.
Environmental considerations further highlight gelatin’s importance. As a byproduct of the meat industry, its production reduces waste. Sustainable sourcing and ethical practices are increasingly prioritized, ensuring gelatin remains a responsible choice for consumers and producers.
If you enjoyed this recipe, you might also like our agar agar powder.
Variants of Gelatin
Gelatin comes in several forms, each suited to specific applications. Powdered gelatin is the most common, ideal for home cooking and industrial use. Sheet gelatin, leaf gelatin, preferred by professional chefs for its precise measurement and smooth texture.
Learn more about gelatin benefits in this search.
Animal-based gelatin varies by source, with pork and beef being the most prevalent. Fish gelatin is an alternative for those avoiding mammalian products. Each type has distinct gelling strengths and melting points, influencing their suitability for different recipes.
| Type | Source | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Powdered | Pork/Beef | General cooking |
| Sheet | Pork/Beef | Professional use |
| Dietary restrictions |
Uses of Gelatin
Gelatin’s culinary uses are vast, ranging from desserts like panna cotta to savory dishes like aspic. It acts as a stabilizer in whipped cream and yogurt, ensuring smooth textures. Confectionery products, such as gummy bears, rely on gelatin for their chewy consistency.
In pharmaceuticals, gelatin capsules are the standard for oral medications. They protect active ingredients from degradation and mask unpleasant tastes. Gelatin also appears in vaccines as a stabilizer, ensuring efficacy during storage and transport.
Cosmetics leverage gelatin for its film-forming and hydrating properties. It is found in face masks, shampoos, and nail treatments. Its ability to bind water helps maintain skin elasticity and hair strength, making it a popular choice in beauty products.
Comparing Gelatin
Gelatin differs from plant-based alternatives like agar-agar and pectin in several ways. While all three provide gelling properties, gelatin offers superior elasticity and melt-in-the-mouth texture. Agar-agar sets firmer and is heat-resistant, making it suitable for vegan recipes.
Animal-derived gelatin is more versatile in culinary applications but may not suit dietary restrictions. Plant-based options cater to vegetarians and vegans but often require adjustments in recipes. Understanding these differences helps in selecting the right gelling agent for specific needs.
Best Practices for Gelatin
When using gelatin, proper hydration is essential. Always bloom powdered gelatin in cold water before dissolving it in warm liquid. This ensures even distribution and prevents clumping. For sheet gelatin, soak it in cold water until pliable, then squeeze out excess moisture.
Temperature control is critical to gelatin’s performance. Avoid boiling gelatin solutions, excessive heat can weaken its gelling ability. Similarly, refrigerate mixtures to set properly. Following these steps guarantees optimal results in both cooking and industrial applications.

Frequently Asked Questions
Gelatin is derived from animal collagen, typically sourced from the bones, skin, and connective tissues of cows, pigs, or fish. It undergoes a process of boiling and drying to create the powdered or sheet form commonly used in cooking.
How is gelatin used in cooking?
Gelatin is primarily used as a gelling agent in recipes like desserts, jellies, and marshmallows. It helps thicken and stabilize liquids, creating a smooth, firm texture when set.
Is gelatin vegetarian or vegan?
Gelatin is not vegetarian or vegan since it is made from animal-derived collagen. Plant-based alternatives like agar-agar or pectin are often used as substitutes.
What are the health benefits of gelatin?
Gelatin is rich in amino acids that support joint health, improve skin elasticity, and promote gut health. It may also aid in digestion and strengthen hair and nails.
Can gelatin be substituted in recipes?
Yes, gelatin can be replaced with alternatives like agar-agar, pectin, or carrageenan. These substitutes work well in vegan or vegetarian recipes but may require adjustments in quantity.
How do you dissolve gelatin properly?
To dissolve gelatin, sprinkle it over cold water and let it bloom for 5-10 minutes. Then, gently heat the mixture until fully dissolved, avoiding boiling to maintain its effectiveness.
What’s the difference between gelatin and collagen?
Gelatin is derived from collagen and is used primarily in cooking. Collagen, on the other hand, is a protein found in connective tissues and is often consumed as a supplement for health benefits.
Are there any side effects of eating gelatin?
While generally safe, some people may experience mild digestive issues or allergic reactions to gelatin. It’s important to consume it in moderation and consult a doctor if concerns arise.
What types of desserts use gelatin?
Gelatin is commonly used in desserts like jellies, panna cotta, marshmallows, and mousses. It provides a smooth, firm texture that enhances the overall consistency of these treats.
Can gelatin be used in savory dishes?
Yes, gelatin is versatile and can be used in savory dishes like aspic or broth to add thickness and structure. It’s a valuable ingredient in both sweet and savory culinary applications.
Conclusion
Understanding what gelatin is and its various applications can greatly enhance your culinary skills and knowledge of its health benefits. Derived from animal collagen, gelatin serves as a versatile ingredient in both sweet and savory dishes, offering unique texture and stability. It’s important to note that gelatin is not suitable for vegetarians or vegans, but alternatives like agar-agar provide excellent substitutes. Beyond cooking, gelatin is praised for its potential health benefits, including improved joint health, skin elasticity, and digestion. Whether you’re making desserts like jellies and mousses or exploring its use in savory recipes, gelatin remains a cornerstone in many kitchens. To ensure success, always dissolve it properly and consider potential substitutions if needed. Now that you’re equipped with this knowledge, try incorporating gelatin into your next culinary creation for a delightful and nutritious experience.